| |
OrgScope Link Types
|
|
 |
|
 |
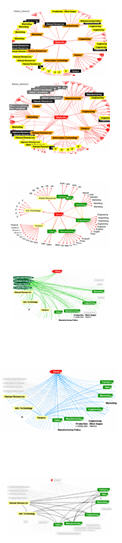
link hooks every base position into a mutually-exclusive classification hierarchy that defines the organization’s terrain
|
|
links gives more accurate picture of reporting load, and may be the source of “small-world” metrics in organizations
|
|
links adds supplier-customer dynamics to the picture of positional responsibilities, and, with A-links, may be basis for complexity metrics
|
|
links are used to map group memberships and, with A-link manager teams, can create affiliation patterns of who knows whom because of a common group
|
|
links are used to map communications flows together with other relationships; they may also, with appropriate use of data mining, show actual information patterns between positions
|
|
links are used to map personal relationships in organization context that are not otherwise accounted for; they may also represent social network data as a layer over the positional communications patterns
|
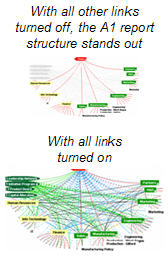
Reporting relationships are only the starting point for mapping the organization. What gives the organization juice are matrices, process dynamics, inter- and intra-group interactions, information flows and personal relationships. However, to make use of the link spectrum, you must be able to filter specific link frequencies in or out to fit the context or explanatory need of a particular network
|
|

